How the feed-in tariff works in Germany for Photovoltaics: Rules, Calculation, and Benefits
The feed-in tariff is a central instrument for promoting renewable energy in Germany. But how exactly does this system work, and what benefits does it offer homeowners, businesses, and industrial clients? In this comprehensive article, you will learn everything about the feed-in tariff, its legal foundations, calculation methods, and how to get the most out of your solar PV system.
What is a feed-in tariff, and why is it important in Germany?
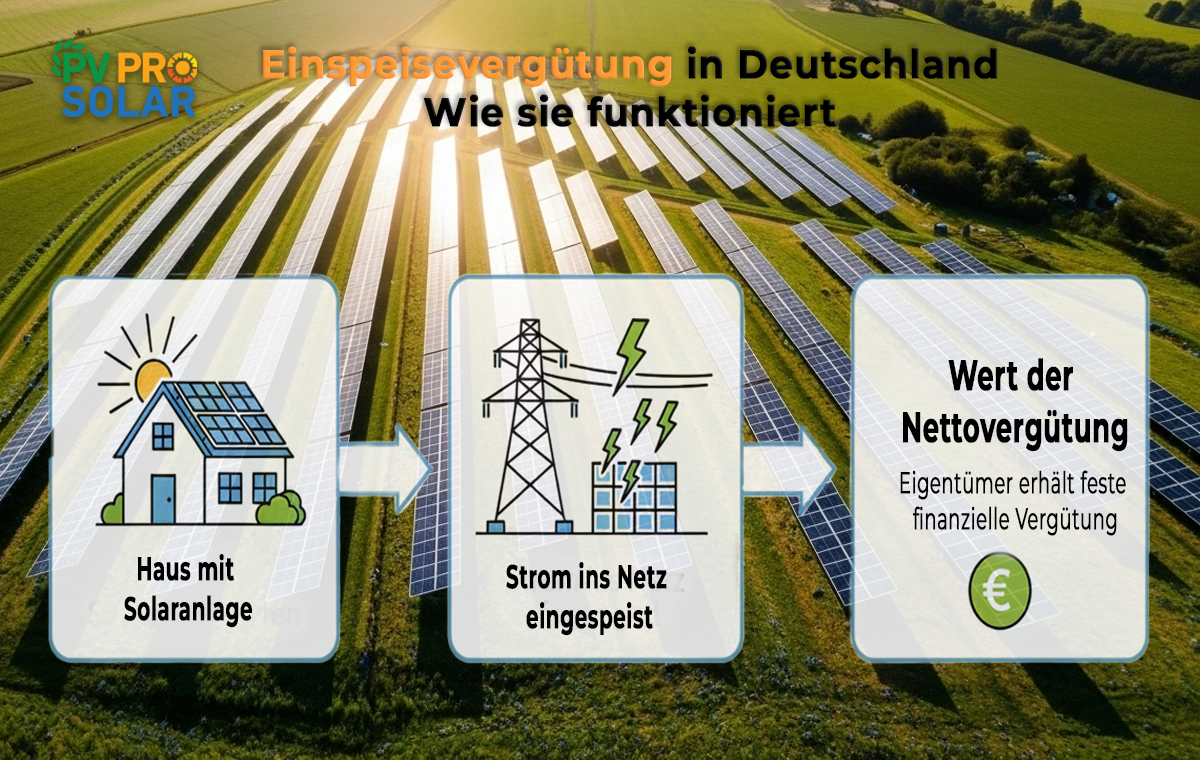
A feed-in tariff is a financial payment that operators of renewable energy systems receive when they feed the electricity they generate into the public grid. This system was introduced to promote the expansion of renewable energy and contribute to a sustainable energy supply. In Germany, the feed-in tariff is a key part of the energy transition.
How does the feed-in tariff work in Germany?
The feed-in tariff is based on the Renewable Energy Sources Act (EEG), which sets the framework for promoting renewable energy. System operators receive a fixed tariff guaranteed for a specific period. The price depends on the type of energy source, system size, and commissioning date.
Who can benefit from the feed-in tariff?
Private individuals, businesses, and industrial plant operators can benefit if they operate a renewable energy system. In Germany, operators of solar PV systems, wind turbines, biogas plants, and hydropower plants are particularly eligible.
How is the feed-in tariff calculated?
The tariff depends on several factors, including system size, type of energy generation, commissioning date, and technical performance. The payment is expressed in cents per kilowatt-hour (ct/kWh) and adjusted annually.
Which renewable energy sources are eligible for the feed-in tariff?
The feed-in tariff applies to electricity from:
- Solar PV
- Wind energy
- Hydropower
- Biomass
- Geothermal energy
Each energy source has specific tariff rates that vary based on efficiency and market developments.
How long does the feed-in tariff last for solar PV systems?
For solar PV systems, the guaranteed feed-in tariff generally lasts 20 years from commissioning, providing investors with planning security and ensuring economic feasibility.
How has the feed-in tariff developed in Germany?
Since its introduction in 2000, the feed-in tariff has undergone several adjustments to respond to rapid technological advances and increasing market penetration. Tariff rates decrease over time to reduce costs and encourage innovation.
What are the legal foundations of the feed-in tariff in Germany?
The feed-in tariff is regulated by the Renewable Energy Sources Act (EEG), which is regularly updated. This law sets the framework, tariff rates, and obligations for grid operators.
What is the market premium model compared to the fixed feed-in tariff?
In addition to the fixed tariff, the market premium model allows operators to sell electricity directly on the market while receiving a premium to bridge the gap to the fixed tariff. This encourages market integration and flexibility.
How to apply for the feed-in tariff in Germany?
Operators must register their system with the Federal Network Agency and submit a feed-in tariff application. It is essential to meet all technical and legal requirements to secure the funding.
How does the feed-in tariff affect the profitability of solar systems?
The feed-in tariff provides operators with a predictable income source, making solar investments financially attractive. The tariff level and electricity cost savings determine the system’s return on investment.
What challenges exist in the feed-in tariff system?
Challenges include:
- Tariff degression
- Integration into the energy market
- Increasing optimization of self-consumption
How does the German government support renewable energy through the feed-in tariff?
The government implements the EEG and adjusts regulations to promote renewable energy expansion and achieve climate protection goals.
How does the feed-in tariff contribute to the energy transition?
By making investments in renewable energy financially attractive, the feed-in tariff supports the shift from fossil fuels to sustainable energy sources and helps reduce CO2 emissions.
What are the latest changes in the feed-in tariff?
Tariff rates are increasingly market-oriented. Flexible systems, such as storage and self-consumption models, are gaining importance.
How does integrating energy storage affect the feed-in tariff?
Energy storage allows better use of self-generated electricity and can increase feed-in tariff revenue by smoothing peaks and increasing self-consumption.
What is the difference between a feed-in tariff and net metering?
While the feed-in tariff offers a fixed payment for electricity fed into the grid, net metering allows offsetting electricity fed and consumed, usually without direct payment.
How do companies and industrial clients benefit from the feed-in tariff?
Besides financial incentives, companies gain brand value, reduce energy costs, and meet sustainability goals through renewable energy deployment.
What alternatives exist to the feed-in tariff in Germany?
Alternatives include:
- Self-consumption models
- Direct marketing
- Investment grants
- Funding programs for energy storage and system integration
How to maximize returns from the feed-in tariff?
- Optimize system size
- Choose the right technology
- Use storage solutions
- Apply effective tax planning
The feed-in tariff is a vital instrument for renewable energy promotion in Germany, providing financial security to private and commercial operators. To fully benefit, investors should stay informed about current regulations, market models, and technical options while carefully planning their solar PV systems.
The feed-in tariff generally applies for 20 years from the commissioning date.
Yes, energy storage can complement the feed-in tariff by increasing self-consumption and smoothing peak loads. How long does the feed-in tariff apply to new solar PV systems?
Can I combine the feed-in tariff with an energy storage system?