Can Solar Panels Work in Winter in Germany? Complete Guide
Many people wonder whether solar panels can reliably generate electricity during the colder months. In Germany—with its long winters, short days, and frequent cloud cover—there’s often uncertainty about the efficiency and economic viability of photovoltaic (PV) systems in winter. However, modern technology has shown that solar panels can work effectively even in winter. In this article, you’ll learn how photovoltaics function during the cold season, which factors are critical, and how you can get the most out of your solar system all year round.
How Much Sunlight Does Germany Get in Winter?
Sunshine duration in Germany varies significantly by season. From November to February, daylight hours average just 8 to 9 hours per day—sometimes even less in northern regions. Cloudy days are also common during these months.
According to the German Weather Service (DWD), the average sunshine hours in January are approximately:
- Hamburg: ~45 hours
- Berlin: ~50 hours
- Munich: ~65 hours
For comparison: In July, these same cities receive around 220 to 250 sunshine hours.
Global solar radiation in Germany averages 200–400 kWh/m² in winter, while in summer it can exceed 1,500 kWh/m². Despite the lower intensity, solar panels still produce electricity in winter because photovoltaic systems use both direct and diffuse sunlight (the light scattered by clouds). Studies show that about 50% of annual global solar radiation in Germany is diffuse light.
Example:
A 10-kWp PV system in Hannover generates an average of 300–400 kWh in January, compared to over 1,200 kWh in July. That means it still reaches 20–30% of its summer output—a notable contribution to household energy needs.
Can Solar Panels Generate Power When Covered in Snow?
Snow plays an important role, especially in southern Germany or high-altitude areas. In general:
- Thin layers of snow still let some light through, allowing limited energy generation.
- Thick snow cover can block sunlight almost entirely.
- Black solar modules heat up more quickly from residual radiation and often clear themselves.
- A tilt angle of 30–40 degrees helps snow slide off naturally. Flat roofs or systems with a low tilt have a higher risk of snow accumulation.
Bonus: Snow can act like a mirror—once the modules are clear, they benefit from reflected light. Research by the University of Applied Sciences Berlin found that after snowfall, some modules generated up to 10% more electricity due to the albedo effect, compared to similar snow-free days.
Real-world case:
A PV system with 8 kWp in Upper Bavaria produced around 400 kWh in February 2022, despite several snowy days. A comparable system in the same region without an optimal tilt angle only managed 320 kWh.
What Temperatures Are Ideal for Solar Panels in Winter?
Many assume that solar panels perform best in summer due to stronger sunlight. In fact, temperature plays a crucial role:
- Silicon solar cells lose voltage in high heat.
- Efficiency drops by about 0.3–0.5% per degree above 25°C.
- In cold weather, voltage increases, improving performance.
So, a sunny winter day at 0°C can actually produce better performance than a hot summer day at 30°C.
Example from Munich:
A 10-kWp system achieved a peak output of 9.7 kW on January 5, 2023, at -2°C. The same system reached only 8.5 kW on July 30, 2023, at 32°C.
How Do PV Systems Compare in Efficiency Between Summer and Winter?
Solar generation is naturally higher in summer due to longer daylight and higher sun angles. However, the cooler air in winter helps improve efficiency.
- Summer output: up to 6 kWh/kWp per day
- Winter output: around 1–2 kWh/kWp per day
A 10-kWp system can generate 10–20 kWh daily in winter—enough to cover the basic consumption of many households.
How Does Daylight Length Affect Electricity Production?
In December, daylight in:
- Hamburg: ~7 hours 40 minutes
- Munich: ~8 hours 20 minutes
By comparison, in June, Munich enjoys over 16 hours of daylight.
Fewer daylight hours naturally mean less time for energy production. However, modern energy storage systems can bridge the gap by storing excess power during the day for use in the evening.
Can Solar Panels Work on Cloudy Winter Days?
Yes. PV systems also utilize diffuse light, not just direct sunlight. Even without clear skies, your panels will continue to generate electricity:
- Partly cloudy: up to 40–60% of rated capacity
- Heavily overcast: typically 10–25% of capacity
This is particularly important in northern Germany, where winters tend to be cloudier.
What Role Does the Tilt Angle of Solar Panels Play in Winter?
Tilt angle is crucial to maximize output during short winter days:
- Ideal for summer: 20–30 degrees
- Better for winter: 30–40 degrees, as the sun is lower in the sky
A steeper angle also helps reduce snow buildup.
Example:
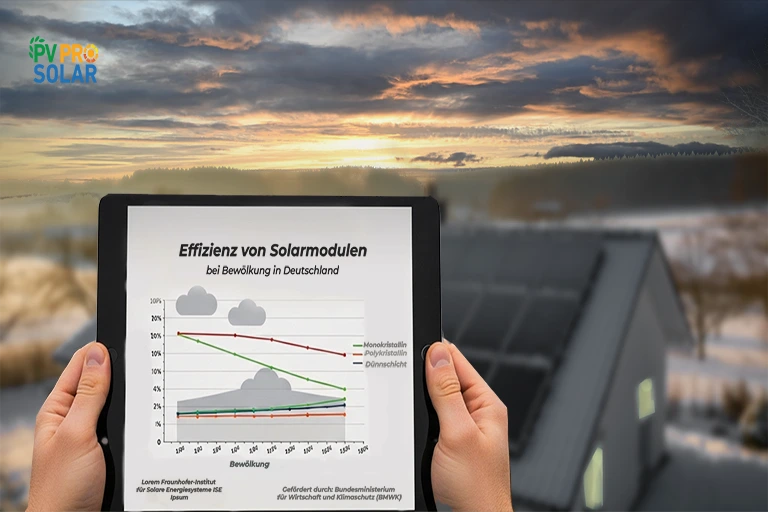
A Fraunhofer ISE study found that systems with a 35° tilt produced up to 15% more electricity in winter than systems tilted at 20°.
Solar panels do work reliably in winter in Germany, even though their output is lower than in summer. In fact, cold air can enhance their efficiency, and modern systems are increasingly able to handle snow and low sunlight conditions.
With smart planning, the right tilt angle, and energy storage solutions, PV system owners can achieve stable energy yields even in the winter months. Photovoltaics remain a sustainable and cost-effective energy solution—all year round.
Yes. While production is lower, solar systems can still cover a significant portion of household demand. Storage solutions help balance the fluctuations.
In most cases, no. The tilt and heat from the modules often clear snow naturally. For thick snow layers, gentle removal can help. Can solar panels generate enough electricity for home use in winter?
Do solar panels need to be cleared of snow in winter?