How Do Solar Panels Work in Germany? A Complete Guide for 2025
Solar panels have become a key pillar of Germany’s energy transition. An increasing number of households and businesses are turning to photovoltaic (PV) systems to reduce their dependence on rising electricity prices and fossil fuels while helping protect the environment. But for many who are interested, one question remains: how do solar panels work in Germany? In this article, we explain the technology, functionality, benefits, and legal framework you need to understand in 2025.
How Are Solar Panels Technically Structured?
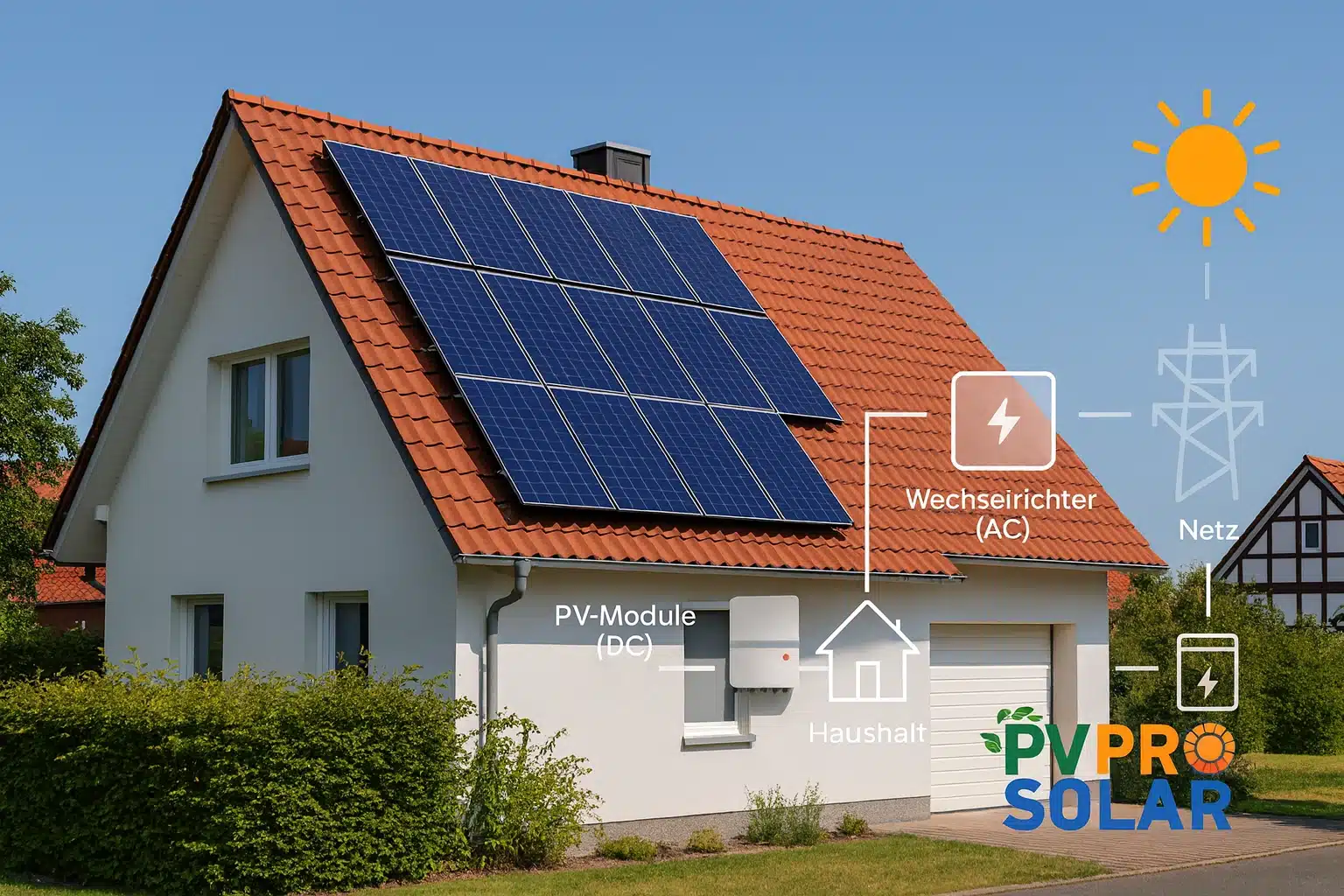
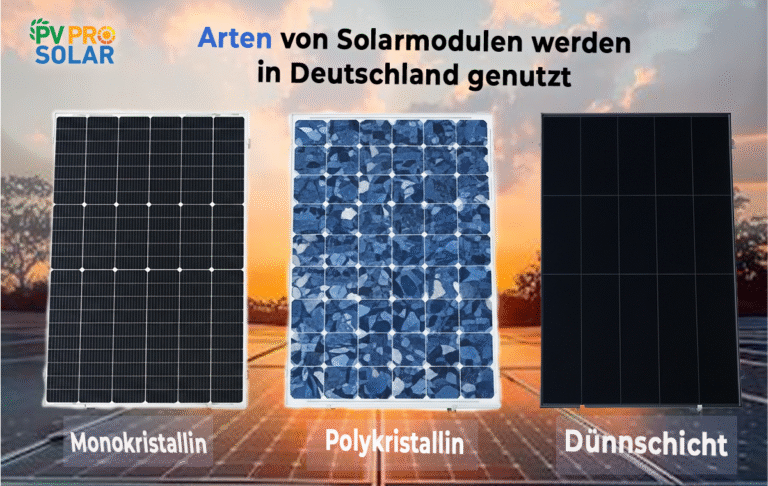
A solar panel system is made up of several components: solar modules (containing numerous solar cells), an inverter, an optional battery storage unit, and a connection to the power grid. The sun provides the necessary radiant energy, which is captured by the individual solar cells.
These modules convert sunlight into direct current (DC). The inverter then transforms this into alternating current (AC), which can be used in your home or fed into the grid. Some systems also include solar thermal collectors that produce heat energy for space heating and hot water. This allows both electricity and heat demands to be met sustainably.
How Does Location Impact Solar Energy Output in Germany?
Location plays a significant role in determining the output of a solar energy system. Annual hours of sunshine vary across Germany – around 1,700 hours in the south and approximately 1,400 in the north. However, solar power remains a viable option across the entire country, thanks to modern solar modules that can efficiently convert even diffused sunlight.
Roof-mounted systems use advanced technology to transform light into electricity – a virtually limitless resource. Expert evaluations year after year confirm that solar panels deliver attractive returns in all regions of Germany.
How Is Sunlight Converted Into Usable Electricity?
The foundation of solar energy is the photoelectric effect: sunlight hits a solar cell, exciting electrons in a thin semiconductor layer, which generates movement. This movement creates voltage, producing electricity.
Multiple solar cells make up a module, and multiple modules form a solar array. The conversion of solar radiation into electricity occurs in every component. The electricity produced can either be used immediately, stored, or fed into the public grid.
The system operates surprisingly simply: sunlight hits the solar cells, which generate electricity. That electricity is then converted by the inverter into household-ready power.
What Roles Do Inverters and Battery Storage Play?
The inverter is the heart of the solar system. It converts the generated direct current into usable alternating current. Without it, no household devices could function on solar power.
Battery storage systems are gaining importance in Germany. They enable you to use your self-generated solar power even during the evening and night, increasing your self-consumption rate to as much as 80%. Some systems are also equipped with additional safety and energy management features.
What Are the Costs of Installing Solar Panels in Germany?
The total cost depends on the system size. A typical 5 kWp system for a single-family home in 2025 costs around €7,500 to €9,500. If a battery storage unit is included, total costs rise to approximately €13,000 to €16,000. Thanks to falling module prices and government subsidies, most systems pay for themselves within 8 to 12 years.
What Subsidies and Regulations Apply in Germany?
Germany offers a variety of support programs such as KfW loans, regional grants, and tax incentives. The Renewable Energy Sources Act (EEG) governs feed-in tariffs. Since 2023, a zero VAT rate applies to small PV systems up to 30 kWp, making these systems even more financially attractive.
What Is the Lifespan of a Solar Panel System?
Most manufacturers offer warranties of 20 to 25 years for their modules. However, in practice, systems often remain functional for more than 30 years. Inverters and battery units typically require replacement every 10 to 15 years.
What Are the Benefits of Solar Panels for Homeowners?
- Cost savings: Significantly lower electricity bills.
- Energy independence: Reduced reliance on volatile electricity prices.
- Sustainability: A direct contribution to climate protection through renewable energy.
- Property value: Homes equipped with solar panels are more attractive to buyers.
What Role Do Solar Panels Play for Businesses and Industry?
Businesses also stand to gain significantly. PV systems reduce operating costs, improve sustainability performance, and enhance competitiveness. More and more companies in Germany are using solar power to achieve carbon neutrality and lower long-term energy expenses.
How Can Solar Panels Be Used Most Effectively in Germany?
- Integration with heat pumps: Use solar power for domestic heating.
- E-mobility: Charge electric vehicles with your own electricity.
- Smart home solutions: Intelligent systems manage power consumption and storage.
Solar panels are one of the most profitable and environmentally friendly investments in Germany. With cutting-edge technology, generous subsidies, and the ability to dramatically cut electricity costs, they’re an excellent choice for both homeowners and businesses. Understanding how solar panels work in Germany empowers you to make the most of these advantages and contribute actively to the country’s clean energy future.
Yes, even in northern regions, solar panels yield high returns because modern systems are efficient at converting diffused light into electricity.
With battery storage and intelligent energy management, a high degree of self-sufficiency is possible. However, complete independence from the grid is technically feasible only with significant investment. Are solar panels worth it in northern Germany despite fewer sunshine hours?
Can I become completely energy independent with a solar panel system?